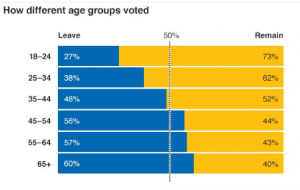
 In last week’s Brexit vote results, there was a tremendous divide between age groups. 73% of voters under the age of 25 voted to remain in the EU, while about 58% over the age of 45 voted to leave.
In last week’s Brexit vote results, there was a tremendous divide between age groups. 73% of voters under the age of 25 voted to remain in the EU, while about 58% over the age of 45 voted to leave.
This generational gap is among the many parallels between Brexit and climate change. A 2014 poll found that 74% of Americans under the age of 30 support government policies to cut carbon pollution, as compared to just 58% of respondents over the age of 40, and 52% over the age of 65.
Inter-generational theft
The problem is of course that younger generations will have to live with the consequences of the decisions we make today for much longer than older generations. Older generations in developed countries prospered as a result of the burning of fossil fuels for seemingly cheap energy.
However, we’ve already reached the point where even contrarian economists agree, any further global warming we experience will be detrimental for the global economy. For poorer countries, we passed that point decades ago. A new paper examining climate costs and fossil fuel industry profits for the years 2008–2012 found:
“For all companies and all years, the economic cost to society of their CO2 emissions was greater than their after‐tax profit, with the single exception of Exxon Mobil in 2008.”
And as political journalist Nicholas Barrett said in a comment that subsequently went viral:
“The younger generation has lost the right to live and work in 27 other countries. We will never know the full extent of the lost opportunities, friendships, marriages and experiences we will be denied. Freedom of movement was taken away by our parents, uncles, and grandparents in a parting blow to a generation that was already drowning in the debts of our predecessors.”
Thirdly and perhaps most significantly, we now live in a post-factual democracy. Read More

 On Thursday the Prime Minister will make the environmental case for Britain’s place in Europe. He is right to bring this important issue to the top of his agenda.
On Thursday the Prime Minister will make the environmental case for Britain’s place in Europe. He is right to bring this important issue to the top of his agenda.
